Marginal Utility Curve Definition In Economics
By adding MUs TU is obtained. Marginal utility is when theres a variance in satisfaction during consumption.

Curve Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Which Doubles As The Axiomatic Download Scientific Diagram
Symbolically MU fracDelta TUDelta X Where MU Marginal Utility.
Marginal utility curve definition in economics. Marginal utility is the added satisfaction a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. Marginal Utility. Law of Equi-Marginal Utility explains the relation between the consumption of two or more products and what combination of consumption these products will give optimum satisfaction.
Marginal utility can be illustrated by the following. Marginal utility theory can be used to derive the demand curve of a household. It may be positive negative or zero.
A curve illustrating the relationship between the marginal utility obtained from consuming a good and the quantity of the good consumedThe marginal utility curve can be used to derived the demand curve which is discussed in detail in the entry on marginal utility and demand. Term marginal utility and demand Definition. The law of equilibrium utility is known by various names.
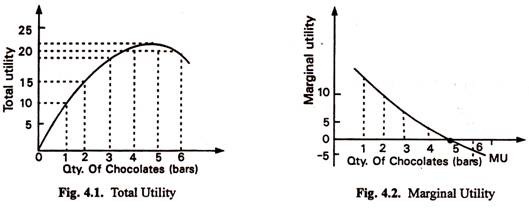
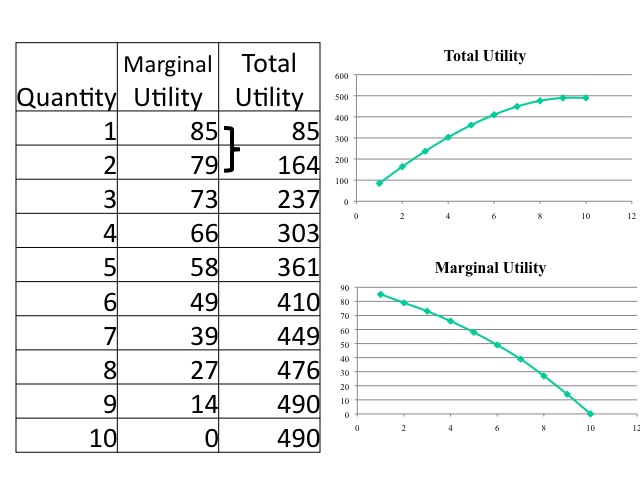
Marginal utility is the incremental increase in utility that results from the consumption of one additional unit. Notice that in the table marginal utility is listed between the columns for total utility because similar to other marginal concepts marginal utility is the change in utility as we go from one quantity to the next. According to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility marginal utility of a good diminishes as an individual consumes more units of a good.
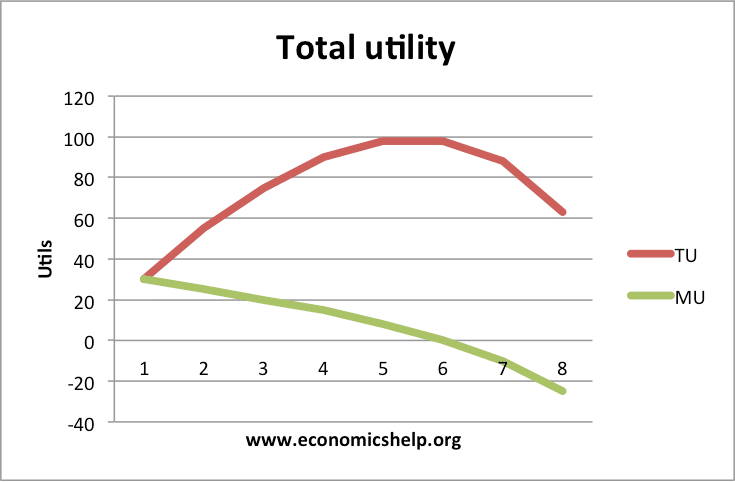
This explanation rests on two propositions. So the c onsumer tastes and balance can also be demonstrated by indifference curves. In the diagram TU is the total utility curve and MU is the marginal utility curve.
In other words as a consumer takes more units of a good the extra utility or satisfaction that he derives from an extra unit of the good goes on falling. Definition and Statement of Law of Equi-Marginal Utility. Marginal utility analysis answers questions such as.
It is named as the Law of Substitution the Law of Maximum Satisfaction the Law of Indifference the. Marginal utility definition economics is represented by MU. Marginal Utility is the additional satisfaction gained by consuming one more unit of a commodity.
The explanation to this can be found in the law of diminishing marginal utility. The concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an item. In economic terms marginal utility of a good or service is the gain from an increase or loss from a decrease in the consumption of that good or service.
Marginal utility then asks how much a one-unit change in a variable will impact our utility that is our level of happiness. In economics utility is the satisfaction or benefit derived by consuming a product. In other words marginal utility is change in total utility due to change in total utility due to change in unit of consumption of the commodity.
The marginal utility they get will therefore influence their willingness to pay for something. Marginal Utility or Marginal Satiety is the additional utility derived from the consumption of an additional unit of a commodity. Price and quantity demanded for most goods and services will be inversely related.
The utility is an economic term used. Marginal utility is the change in the total utility that results from unit one unit change in consumption of the commodity within a given period of time. Here both TU and MU are the same.
An explanation of the law of demand and the negatively-sloped demand curve can be found in the analysis of marginal utility and especially the law of diminishing marginal utility. When we assume one util is valued at 1 dollar y-axis util change to price From budget line and indifference curve we can derive the PCC- price consumption curve. For example purchasing more than one needs brings little satisfaction as the purchaser feels it is wasted.
The marginal utility curve shows zero and negative levels of marginal utility whereas total utility curve shows maximum and constant total utility level. Therefore Marginal Utility the addition made to the Total Utility by consuming one more unit of a commodity. The utility which a consumer obtains by the consuming extra units of the commodity is known as marginal utility.
The law of equi-marginal utility is simply an extension of law of diminishing marginal utility to two or more than two commodities. For example when a person increases the consumption of eggs from one egg to two. An indifference curve shows the various combinations of Article X and Article Y that produce the same degree of utility or satisfaction to the consumer.
When the consumer consumes 2nd unit of goods TU increases to 18 utils from 10 utils and MU decreases to 8 utils. The idea of marginal value is an important consideration when making production or purchasing decisions. MU x TU Q for continuous series OR MU x TUn TUn-1 for discrete series The marginal utility tends to decrease with consumption but it can be zero depending upon the good consumed.
As the consumer consumes the first unit of commodity she obtains 10 utils of utility. The normal demand curve slopes downward from left to right showing that consumers are prepared to buy more at a lower price than a higher price. The Marginal Utility Theory and Indifference Curve Analysis explained why DD curve is downward sloping and can be used to derived the demand diagram.
Hence the individual demand curve will be downward-sloping. Marginal Utility Change in total utilityChange in number of units consumed. Thus the marginal utility of a good or service describes how much pleasure or satisfaction is gained from an increase in consumption.
Higginss marginal utility curve is plotted in Panel b of Figure 71 Total Utility and Marginal Utility Curves The values for marginal utility are plotted midway between. Term marginal utility curve Definition. The formula to find marginal utility definition economics is.
Thus a curve of indifference superior to others which represents a. In other words marginal utility measures incremental utility received from one additional unit of consumption. Marginal utility in economics the additional satisfaction or benefit utility that a consumer derives from buying an additional unit of a commodity or serviceThe concept implies that the utility or benefit to a consumer of an additional unit of a product is inversely related to the number of units of that product he already owns.
Where I is the income of the consumer. TU Total Utility. See also Scope of Microeconomics Meaning and Nature of Microeconomics.
If there are diminishing marginal returns then peoples willingness to pay will also decline.
Oscar Education Economics Total Utility And Marginal Utility

Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Dmu Definition Explanation Importance Criticism
Total Utility Tu And Marginal Utility Mu Difference Definition And Explanation Formula Example Scedule Table Curve Diagram Economicsconcepts Com

Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Concept Assumption Causes And Issues

Utility Maximisation Economics Help

When The Marginal Utility Is Zero What Is The Total Utility Study Com
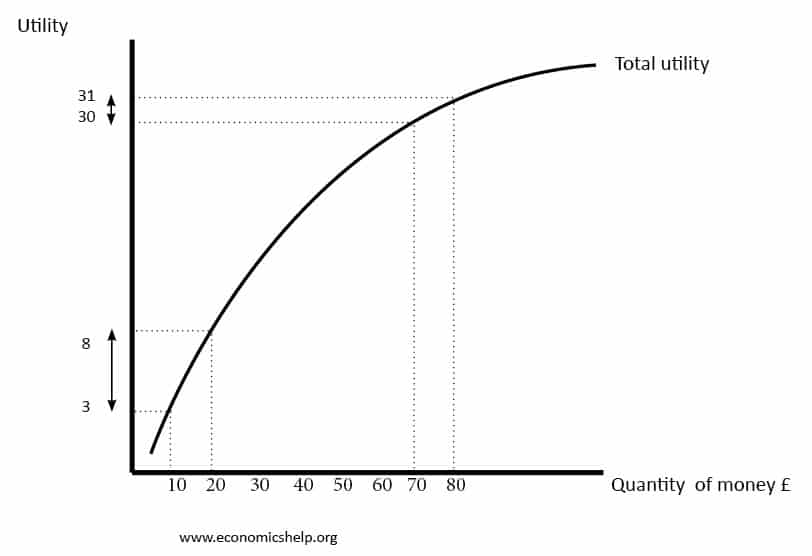
Diminishing Marginal Utility Of Income And Wealth Economics Help
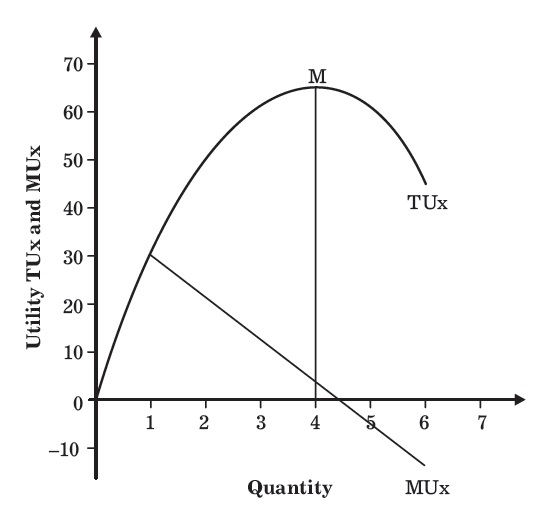
What Is Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Assumptions

Diminishing Marginal Utility An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
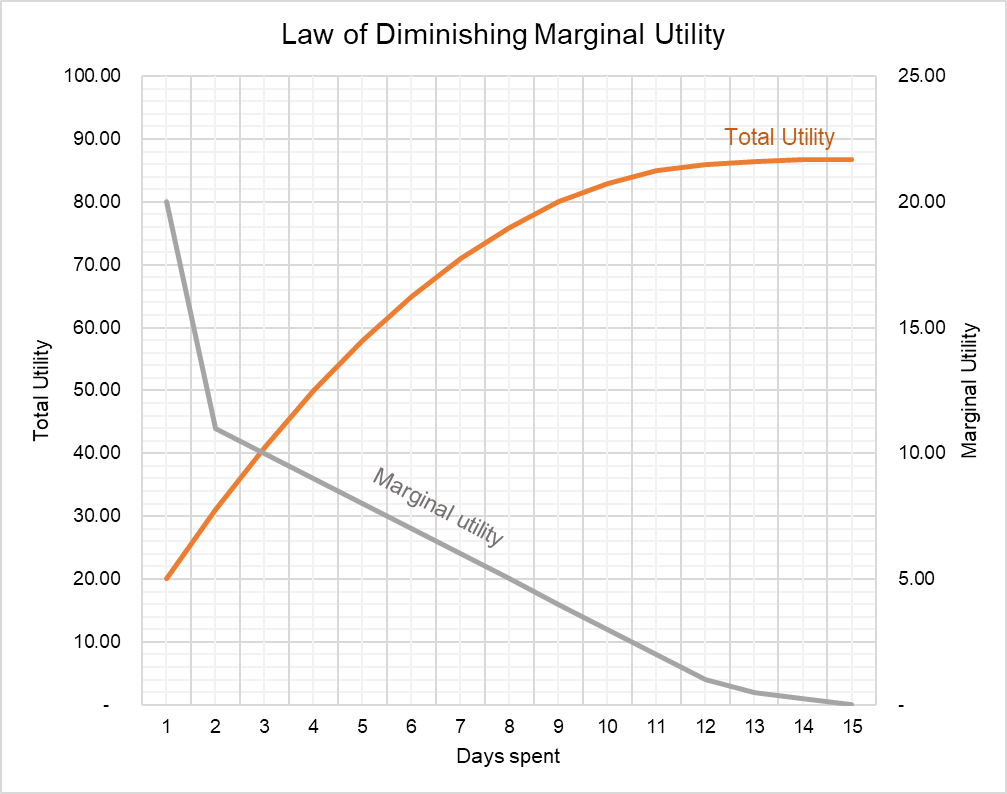
Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Chart And Example

Total Utility And Marginal Utility Forestrypedia
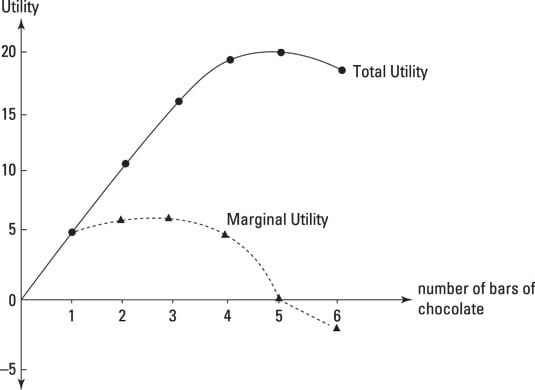
Marginal Utility And The Marginal Unit Dummies


Post a Comment for "Marginal Utility Curve Definition In Economics"