Diminishing Marginal Utility Definition And Example
This law can be explained by taking a very simple example. Explanation and example of law of diminishing marginal utility.
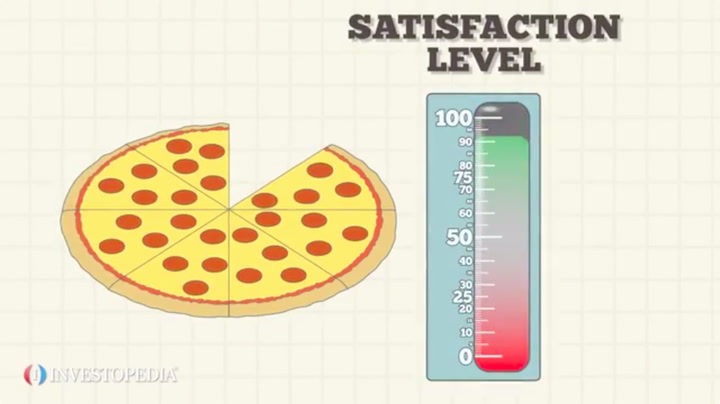
Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Explained
The fall in marginal utility as consumption increases is known as decreasing marginal utility.
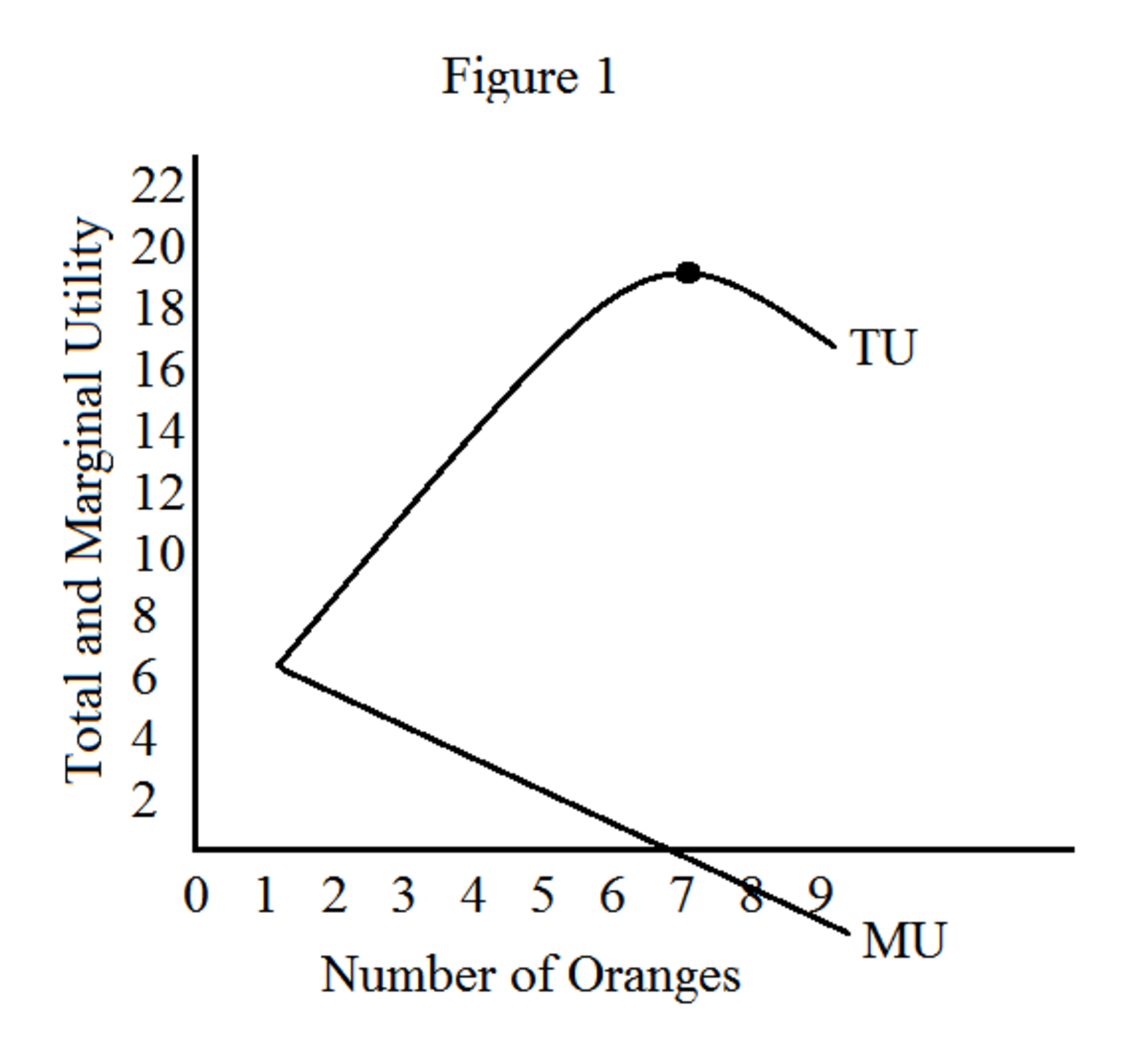
Diminishing marginal utility definition and example. Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility - Definition Examples Graph For example if a hungry person eats a pizza for lunch and then eats more pizza for dinner the law. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as an individual increases consumption of a given product within a set period of time the utility gained from. Generally speaking utility refers to the degree of pleasure or satisfaction or removed discomfort that an individual receives from an economic act.
Diminishing marginal utility is the decline of enjoyment from consuming or buying one additional good. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility states that if the consumption of a good or service increases the satisfaction derived gradually increases but at a decreasing rate to the point where it reaches zero. Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Definition The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as consumption increases the marginal utility derived from each additional unit declines.
He goes to the market and buys one glass of water. Marginal Utility Change in total utilityChange in number of units consumed. If a third is eaten the satisfaction will be even less.
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that- As a consumer consumes more and more units of a specific commodity the utility from the successive units goes on diminishing. Marshall who was the famous exponent of the marginal utility analysis has stated the law of diminishing marginal utility as follows. Marginal Utility is the change in the utility derived from the consumption of an additional unit of a.
Suppose a man is very thirsty. The law of diminishing marginal utility means that the total utility increases but at a decreasing rate. For example three bites of candy are better than two bites but the twentieth bite does not add much to the experience beyond the nineteenth and could even make it worse.
Marginal Utility is the enjoyment a consumer gains from each additional unit they consume. It helps companies figure out the number of products a consumer is eager to buy and assess how satisfaction influences consumer. There are lots of topical examples of diminishing returns some of which have possibly significant economic and social.
Diminishing marginal utility refers to the phenomenon that each additional unit of gain leads to an ever-smaller increase in subjective value. Marginal utility starts to diminish after each unit consumed as enjoyment of another unit declines. The glass of water gives him immense pressure or we say the first glass of water has great utility for him.
Marginal utility is when theres a variance in satisfaction during consumption. Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Definition and Statement of the Law The law of diminishing marginal utility describes a familiar and fundamental tendency of human behavior. The formula for marginal utility is change in total.
Diminishing marginal utility is when a customer becomes less satisfied with a business or product with each interaction they have with themit. The law of diminishing marginal utility explains that as a person consumes an item or a product the utility benefit or use that they get from the product decreases as they consume more of it 1. Marginal utility is a measure that defines an additional benefit a customer receives from one more unit of a product or service.
For example bread and butter are consumed in a ratio and any imbalance in the ratio of the two will give diminishing marginal utility to the consumer. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility states that the amount of satisfaction provided by the consumption of every additional unit of a good decrease as we increase the consumption of that good. What is utility example.
Nature of Human Behavior It is the nature of human behaviour that a consumer will consume more of those goods that he has not consumed and less of those goods he has already consumed. Economists speak of the law of diminishing marginal utility which means that the first unit of consumption of a product or service has more utility than the second and subsequent units with a continuous reduction for larger quantities. Total satisfaction is maximised when marginal utility is zero.
Consuming one candy bar may satisfy a persons sweet tooth. The additional benefit which a person derives from a given increase of his stock of a thing diminishes. If a second candy bar is consumed the satisfaction of eating that second bar will be less than the satisfaction gained from eating the first.
The law of diminishing marginal utility means that the total utility increases but at a decreasing rate.
Assumptions And Importance Of Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Msrblog
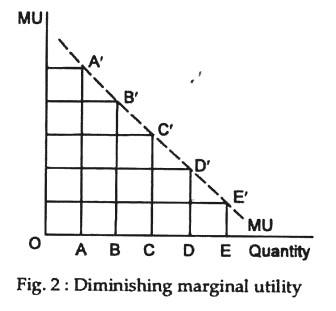
Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Consumption
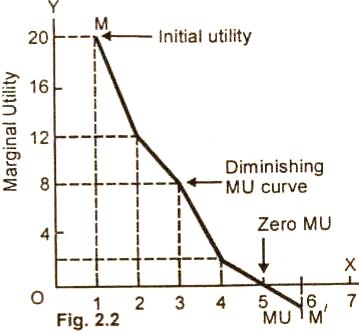
Is The Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility True Stephen Hicks Ph D

What Is Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Definition And Meaning Business Jargons

What Is Diminishing Marginal Utility Definition Meaning Example

Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Dmu Definition Explanation Importance Criticism

Diminishing Marginal Utility An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
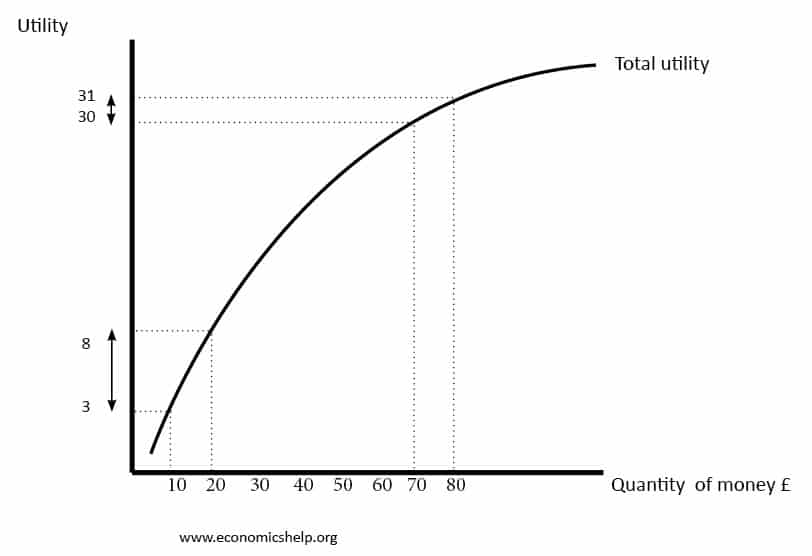
Diminishing Marginal Utility Of Income And Wealth Economics Help
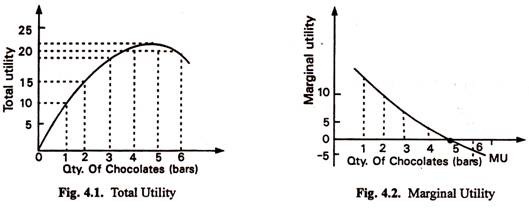
Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Concept Assumption Causes And Issues
Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Microeconomics Class 11 Notes

What Is Diminishing Marginal Utility Pdfshare
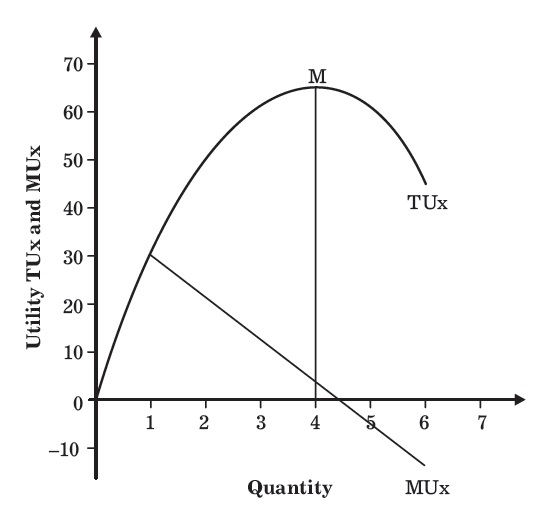
What Is Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Assumptions
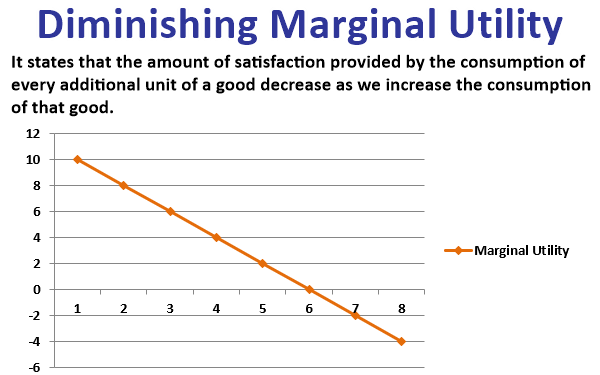
Graphical Illustration Of Law Of Demand Download Illustration 2020

Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Tutor S Tips
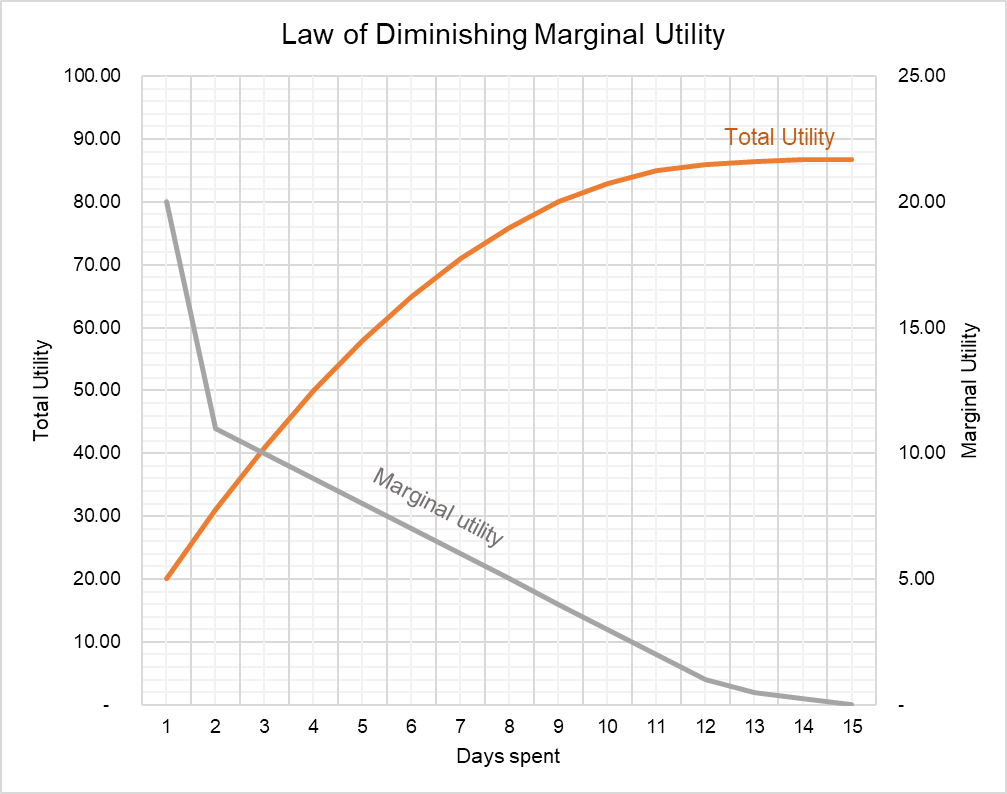
Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Chart And Example
Post a Comment for "Diminishing Marginal Utility Definition And Example"