Cardinal Utility Theory Of Demand
The cardinal utility theory or approach was proposed by classical economists Gossen Germany William Stanley Jevons England Leon Walras France and Karl Menger Austria. Cardinal utility analysis is the oldest theory of demand which provides an explanation of consumers demand for a product and derives the law of demand which establishes an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded of a product.

Consumer Behavior Analysis Cardinal Utility Approach
Ii Utilities of different commodities are independent.
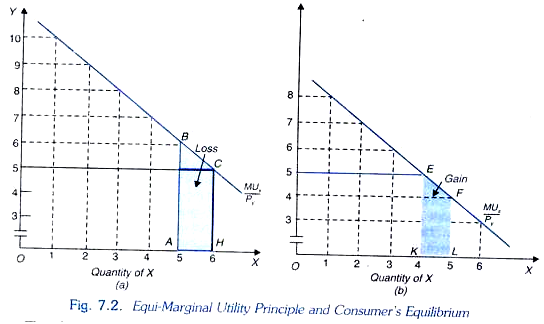
Cardinal utility theory of demand. Cardinal utility measures that satisfaction in units called utils. The derivation of demand is based on the axiom of diminishing marginal utility. The fundamental condition of maximum satisfaction or utility is the equimarginal principle.
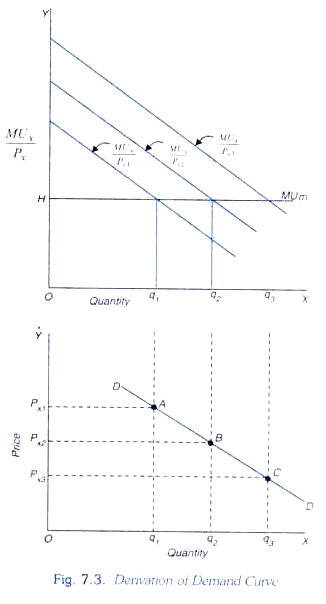
Derivation of Demand Curve. The goods we can say possess independent utilities and are additive. The assumption is that it is possible to place numerical values on utility an assumption that may seem questionable.
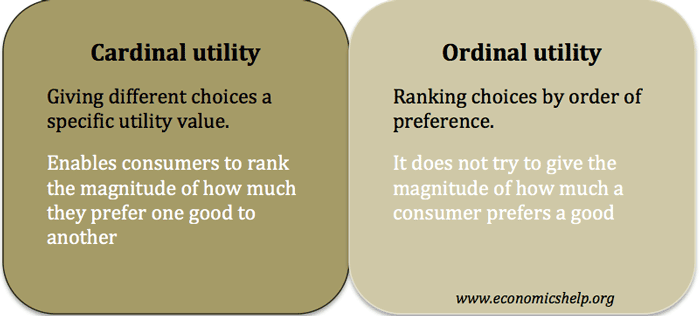
Ordinal utility ranks a series of preferences without measuring how much more valuable one option is than another. Cardinal utility analysis is the oldest theory of demand which provides an explanation of consumers demand for a product and derives the law of demand which establishes an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded of a product. The law of diminishing MARGINAL UTILITY states that as the amount of a good consumed increases the MARGINAL UTILITY of that good tends to diminish.
This is also unrealistic. Remember that utils are abstractions because they arent something in the physical world like inches or pounds. Cardinal Utility Consumer Behavior I.
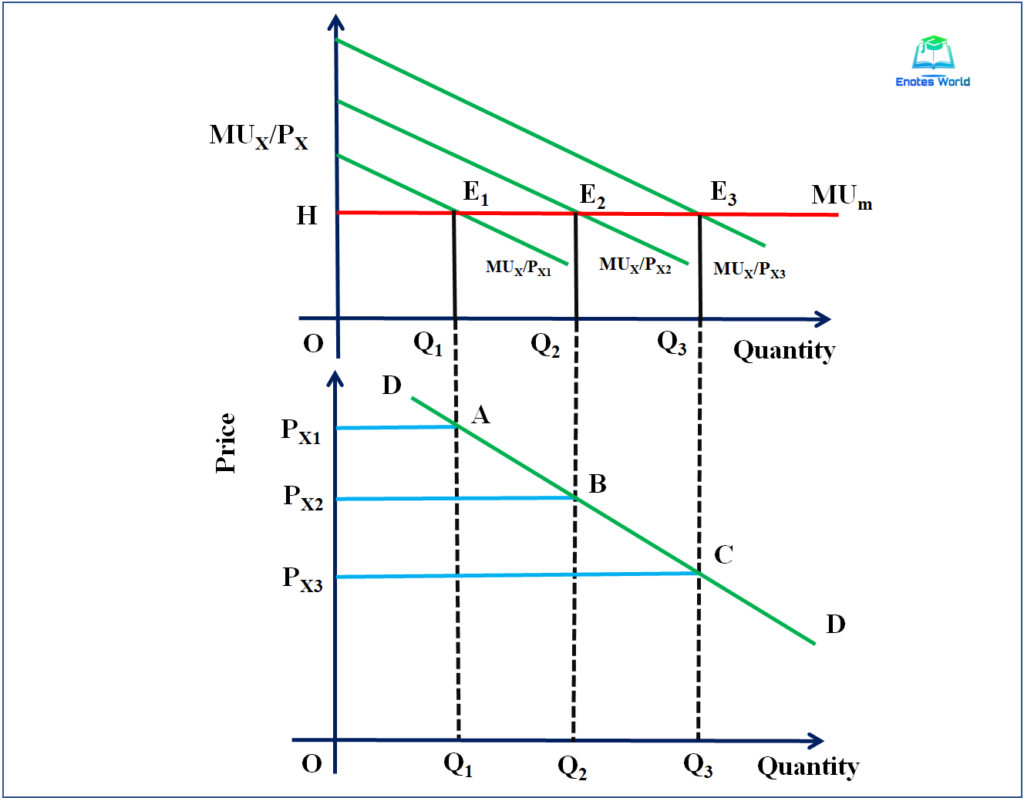
The marginal utility of commodity x may be depicted by a line with a negative slope figure 22. Cardinal utility analysis is the oldest theory of demand which provides an explanation of consumers demand a product and derives the law of demand which establishes an inverse relationship between price and quality demand of a product. In such a point the consumer is consuming the OQ 1 quantity of X.
Both approaches are good enough in different cases but the ordinal utility approach is better because it uses ranks according to which some choices are more preferable than other. Cardinal Utility explains that the satisfaction level after consuming a good or service can be scaled in terms of countable numbers. According to Lipsey and Crystal The satisfaction a consumer receives from consuming a product is called utility.
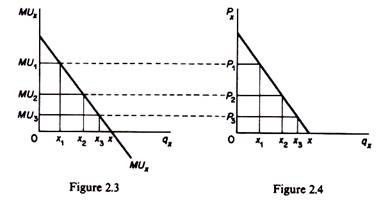
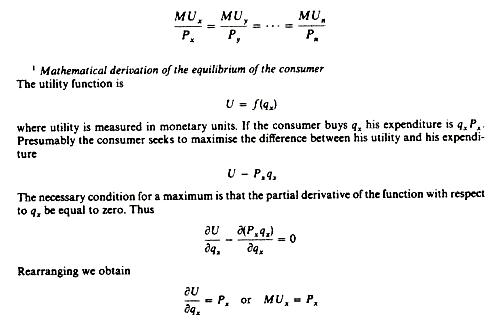
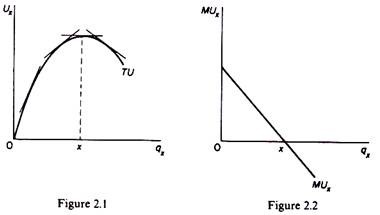
Derivation of the Demand of the Consumer. Utility is the total benefit that a person gets from the consumption of goods and services. Geometrically the marginal utility of x is the slope of the total utility function U fq x.
Cardinal utility theory approaches consumer demand from the standpoint of consumer utility wherein demand is dependent upon factors of utility price income substitutes and complementary goods. Suppose when the price of commodity X is. Economists have developed the concept of cardinal utility to deal with the measurement issue of utility.
Utility 21 Meaning and Characteristics Utility is a property common to all commodities consumed by a person. I Utility is cardinally measurable. If thought logically a price of a product affects the demand of any product.
Cardinal Utility Lets assume that there are only two consumption goods good X cans of coca-cola and good Y cups of popcorn. There are some more theories which can be applied to prove the demand theory. In the utility analysis of demand the following assumptions are made.
Utility can be positive and negative. The theory of demand can be proved by the help of cardinal marginal utility. We have two approaches to utility analysis in economic theory.
It has no physical or material existence. Derivation of demand curve by using Cardinal utility theory Lecture by Faizan Noor. Derivation of demand curve by using Cardinal utility theory Lecture by Faizan Noor Bhutta - YouTube.
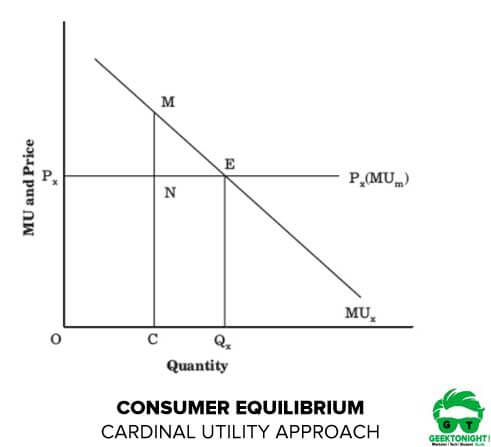
And they measure this satisfaction or utility in utils. Utility has nothing to do with Page 4 Theory of Demand Cardinal. In the upper part of the figure when the price of commodity X is P X1 the equilibrium exists at point E 1 and where MU X P X1 MU m condition is fulfilled.
According to the Cardinalist school the utility which is derived from the consumption of a good is a function of the quantity of that good alone. 2 A cardinal theory of value For completeness we recall Afriats seminal 1967 theorem on rationalizing con-sumer demand data prxrr 12N with an ordinal utility function and the BrownandCalsamiglia2007extensionofAfriatstheoremtorationalizingconsumer demand data with a cardinal utility function ie a quasilinear utility function. There are a few principle factors which are responsible for influencing the demand of a product and supply of the.
The neo-classical economist developed the theory of consumption based on the assumption that utility is measurable. The utility approach to consumer demand theory is based on the assumption of cardinal utility while the indifference curve approach is based on ordinal utility. Derivation of Demand Curve under Cardinal Utility AnalysisTwo Commodities Case.
Iv Utility gained from the successive units of a commodity diminishes. Iii The marginal utility of money to the consumer remains constant. Ordinal utility is generally the preferred method of measuring utility.
The cardinal utility approach derives the demand curve based on the ceteris paribus assumption. Utility and Demand Dr. The consumer should be able to identify the thing what is good and what is bad.
If does not depend at all upon the quantity consumed of other goods. The Cardinal Utility approach is propounded by neo-classical economists who believe that utility is measurable and the customer can express his satisfaction in cardinal or quantitative numbers such as 123 and so on. Cardinal utility analysis is the oldest theory of demand which provides an explanation of consumers demand for a product and derives the law of demand which establishes an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded of a product.
The theory has ignored the substitution and income effect and their effect on the derivation of the. The total utility increases but at a decreasing rate up to quantity x and. Cardinal utility measures how much more preferable one option is in comparison to another.
The Cardinal Utility Theory Explained With Diagram
The Cardinal Utility Theory Explained With Diagram
Consumer S Behaviour Cardinal Utility Analysis Explained With Diagram

Derivation Of Demand Curve Under Cardinal Utility Analysis

Derivation Of Demand Curve Under Cardinal Utility Analysis
The Cardinal Utility Theory Explained With Diagram

Basic Assumption Of Marshallian Utility Analysis Qs Study
Derivation Of The Demand Curve In Terms Of Utility Analysis Assumptions Derivation Of Demand Curve In The Case Of A Single Commodity Derivation Of The Demand Curve In The
What Is Cardinal Ordinal Utility Definition Assumptions

Derivation Of Demand Curve Under Cardinal Approach
Consumer S Behaviour Cardinal Utility Analysis Explained With Diagram
Cardinal And Ordinal Utility Economics Help
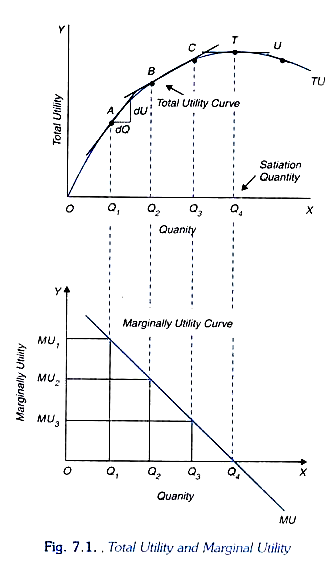
Consumer S Behaviour Cardinal Utility Analysis Explained With Diagram
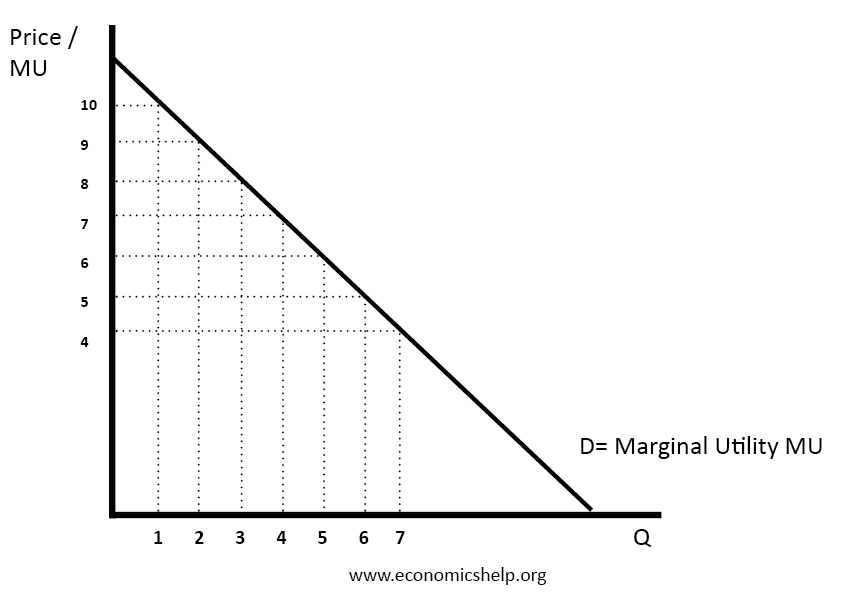
Cardinal And Ordinal Utility Economics Help

Cardinal Utility Approaches To Study The Consumer Behavior Ppt Download
Post a Comment for "Cardinal Utility Theory Of Demand"